0x00 所需工具
Android Studio 2.3.2、NDK、CMake、LLDB
0x01 概念说明
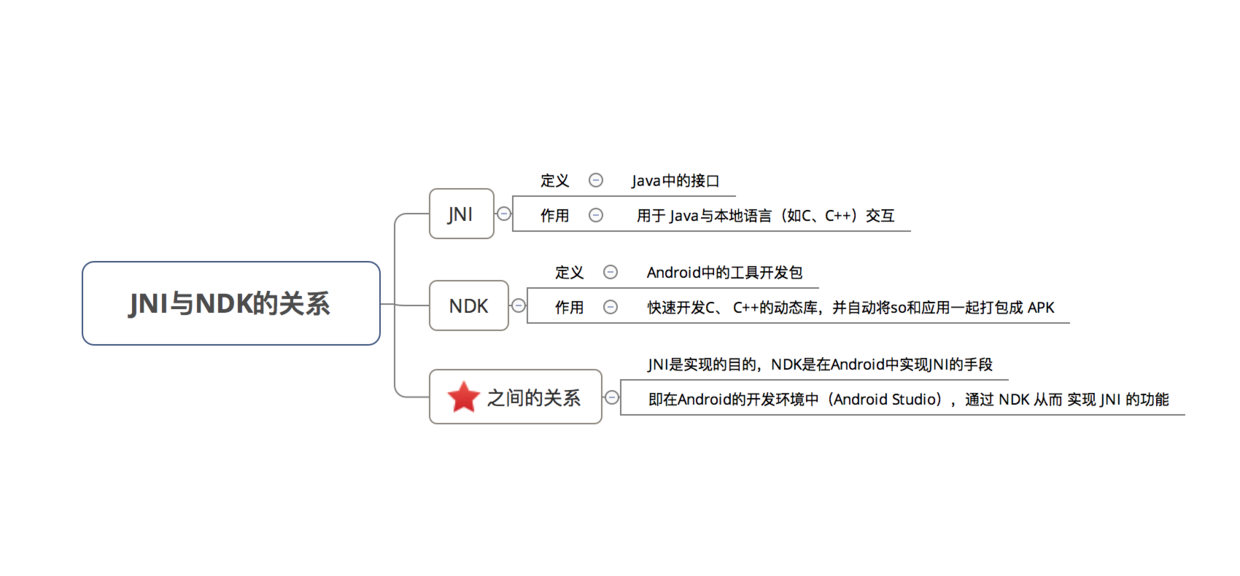
1、NDK(WNative Development Kit)
NDK 是一系列工具的集合,帮助开发者快速开发 C/C++ 的动态库。Android程序运行在Dalvik虚拟机中,NDK允许用户使用类似 C/C++ 之类的原生代码语言执行部分程序。NDK包括从 C/C++ 生成原生代码库所需要的工具和build files。 将一致的原生库嵌入可以在Android设备上部署的应用程序包文件(application packages files ,即.apk文件)中。支持所有未来Android平台的一系列原生系统头文件和库
为何要用到NDK?
概括来说主要分为以下几种情况:
- 代码的保护。由于 apk 的 java 层代码很容易被反编译,而 C/C++ 库反汇难度较大。
- 提高程序的执行效率。将要求高性能的应用逻辑使用 C 开发,从而提高应用程序的执行效率。
- 便于移植。用 C/C++ 写得库可以方便在其他的嵌入式平台上再次使用。
在Android Studio 2.2 之后,工具中增加了 CMake 的支持,你可以这么认为,在 Android Studio 2.2 之后你有2种选择来编译你写的 c/c++ 代码。一个是 ndk-build + Android.mk + Application.mk 组合,另一个是 CMake + CMakeLists.txt 组合。这2个组合与Android代码和c/c++代码无关,只是不同的构建脚本和构建命令。本篇文章主要讲解后者的组合。(也是Android现在主推的)
参考NDK
2、CMake
参考CMake
3、LLDB
是一个高效的c/c++的调试器,是与LLVM编译器一起使用,提供了丰富的流程控制和数据检测,有效的帮忙我们调试程序。LLDB也已经取代GDB成为XCode的默认调试器,Android Studio中也可以使用LLDB调试NDK程序,在Android Studio也中可以LLDB,从SDK Tools中下载LLDB最新版本,配合Android Studio和gradle-experimental一起调试NDK项目,会更加的方便。
4、JNI
定义 Java Native Interface,即 Java 本地接口,使得 Java 与本地其他类型语言 C/C++ 交互
特别注意
- JNI是 Java 调用 Native 语言的一种特性
- JNI 是属于 Java 的,与 Android 无直接关系
5、ABI
ABI(Application binary interface)应用程序二进制接口。不同的 CPU 与指令集的每种组合都有定义的 ABI (应用程序二进制接口),一段程序只有遵循这个接口规范才能在该 CPU 上运行,所以同样的程序代码为了兼容多个不同的CPU,需要为不同的 ABI 构建不同的库文件。当然对于 CPU 来说,不同的架构并不意味着一定互不兼容。
- armeabi 设备只兼容 armeabi;
- armeabi-v7a 设备兼容 armeabi-v7a、armeabi;
- arm64-v8a 设备兼容 arm64-v8a、armeabi-v7a、armeabi;
- X86 设备兼容 X86、armeabi;
- X86_64 设备兼容 X86_64、X86、armeabi;
- mips64 设备兼容 mips64、mips;
- mips 只兼容 mips;
6、NDK与JNI的关系
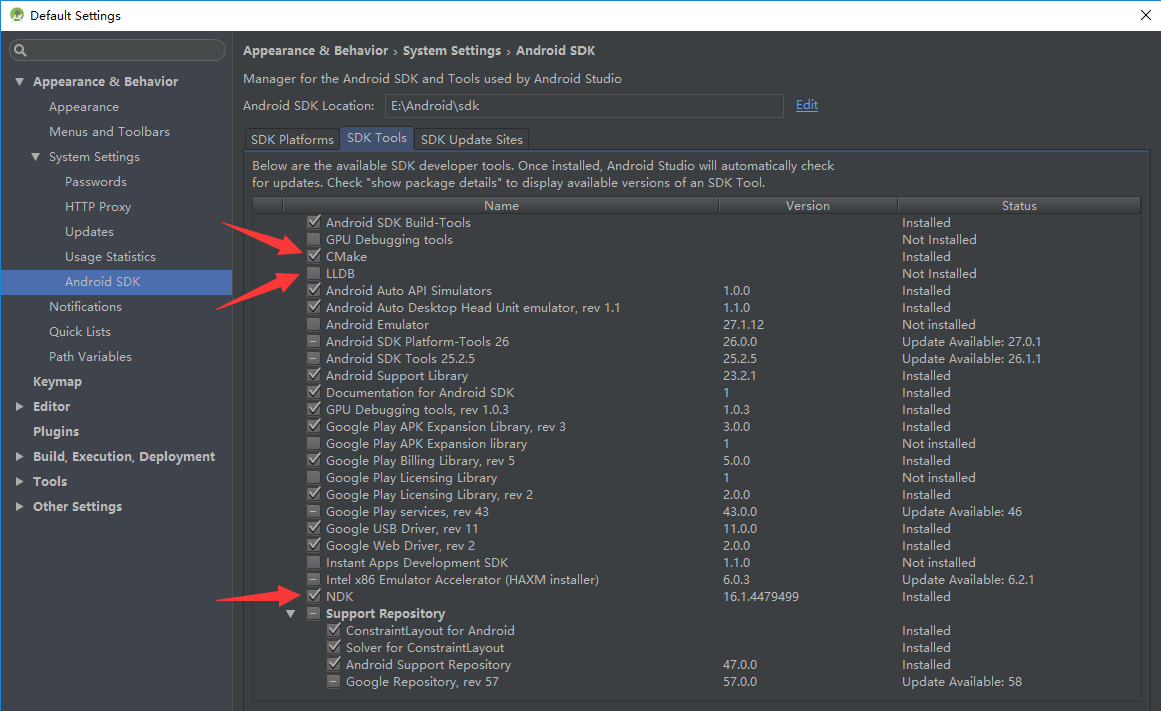
0x02 环境安装(Windows)
主要是 NDK、CMake必须安装
0x03 配置文件与代码讲解
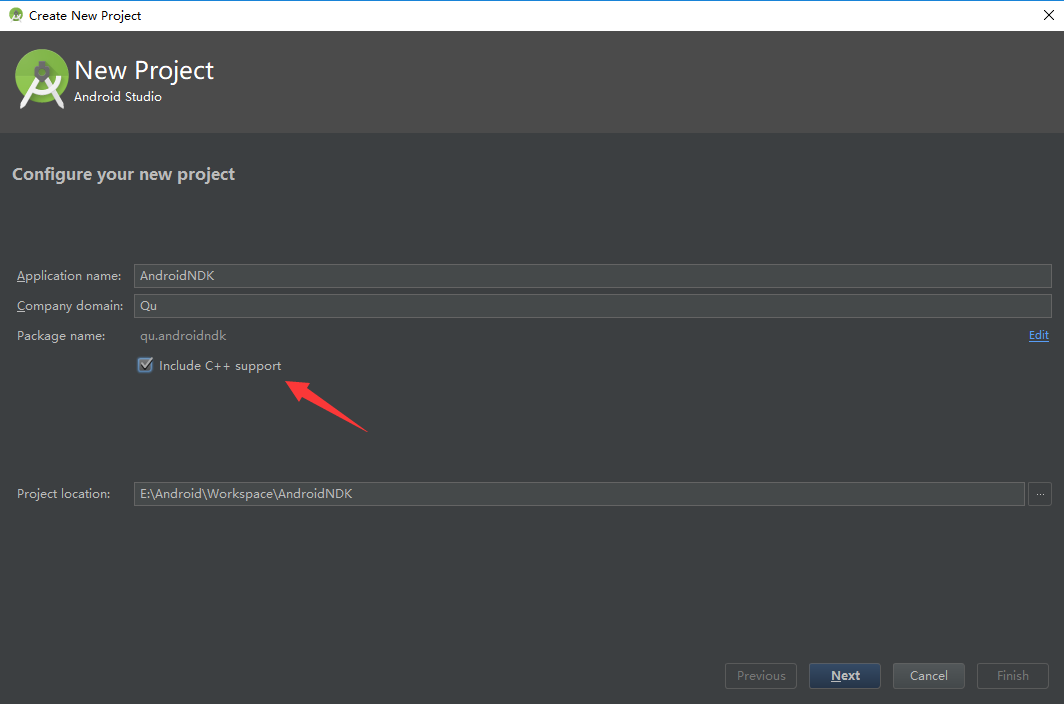
1、新建项目,请勾选Include C++ support
2、其他配置项
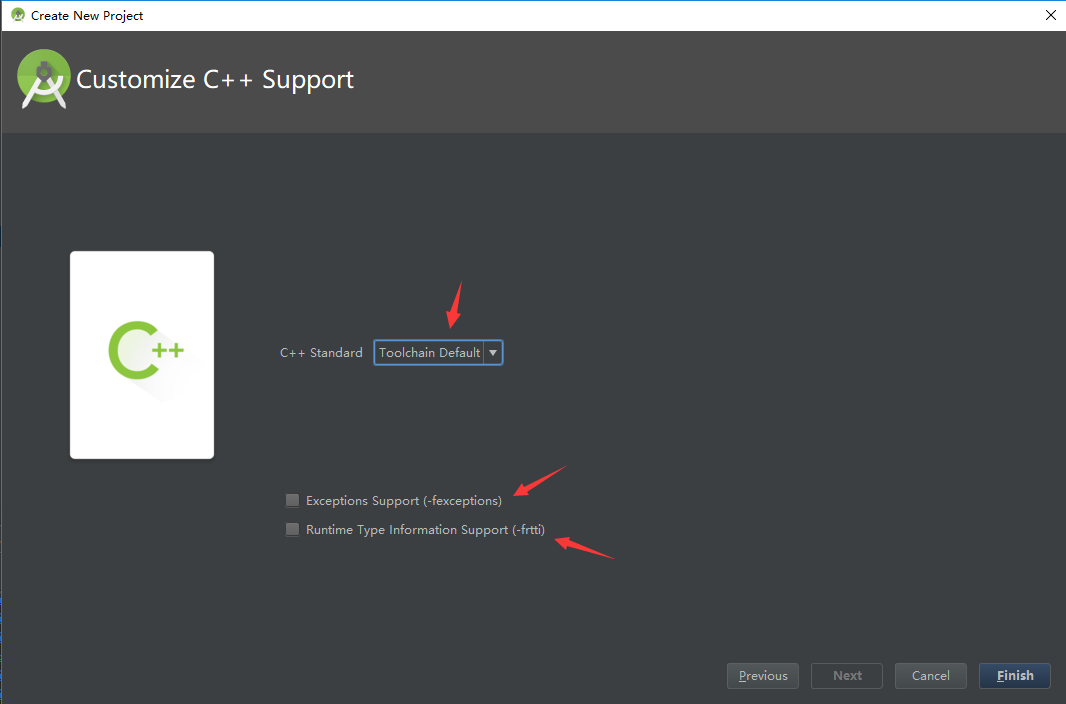
- C++ Standard是让我们选择C++标准
- Exceptions Support是添加C++中对于异常的处理,如选中,Android Studio会 将 -fexceptions标志添加到模块级build.gradle文件的cppFlags中,Gradle会将其传递到CMake
- Runtime Type Information Support是启用支持RTTI,即运行时类型信息,是多态的主要组成部分, 通过运行时(runtime)确定使用的类型,执行不同的函数,复用(reuse)接口. dynamic_cast<>可以使基类指针转换为派生类的指针,通过判断指针的类型,可以决定使用的函数。 typeid(),可以判断类型信息,判断指针指向位置,在多态中,可以判断基类还是派生类。 如选中,Android Studio会将-frtti标志添加到模块级build.gradle文件的cppFlags中,Gradle会将其传递到 CMake。 上面这段摘自网络,意思还不是很理解,等后面学习C++时再继续研究。
点击完成,等待一会,项目可立即运行,屏幕会显示“Hello from C++”
- 以下为完整目录结构
3、代码讲解
- 在 app 模块中新建了一个 cpp 文件夹放置 C/C++ 文件,此处默认的文件为native-lib.cpp
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_qu_androidndk_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(
JNIEnv *env,
jobject /* this */) {
std::string hello = "Hello from C++";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
extern “C” 是告诉编译器按照C语言的规则来编译我们下面的代码
- 在app 模块下建了一个 CMakeLists.txt 文件用于定义一些构建行为,代码如下
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp )
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
native-lib
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib} )
上面大部分为注释内容,最核心的就那么几句
(a) cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1) 用来设置在编译本地库时我们需要的最小的cmake版本,AndroidStudio自动生成。
(b) add_library用来设置编译生成的本地库的名字为native-lib,SHARED表示编译生成的是动态链接库,src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp表示参与编译的文件的路径,这里面可以写多个文件的路径。
(c) find_library 是用来添加一些我们在编译我们的本地库的时候需要依赖的一些库,由于cmake已经知道系统库的路径,所以我们这里只是指定使用log库,然后给log库起别名为log-lib便于我们后面引用,此处的log库是我们后面调试时需要用来打log日志的库,是NDK为我们提供的。
(d) target_link_libraries 是为了关联我们自己的库和一些第三方库或者系统库,这里把我们把自己的库native-lib库和log库关联起来。
- 在 app 模块对应的build.gradle文件中增加了一些配置
externalNativeBuild { cmake { cppFlags "-frtti -fexceptions" } } - cppFlags 在前面有提到,如果选择了 Exceptions Support 、 Runtime Type Information Support 里面就会添加这两个参数
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "CMakeLists.txt"
}
}
-
指定 CMakeLists.txt 文件的路径,由于build.gradle文件和 CMakeLists.txt 文件在同一目录下,所以此处就直接写文件名即可
-
最终在MainActivity.java 文件中我们看到了函数的调用过程如下
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { // Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup. static { System.loadLibrary("native-lib"); } @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // Example of a call to a native method TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text); tv.setText(stringFromJNI()); } /** * A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library, * which is packaged with this application. */ public native String stringFromJNI(); }
这里主要做了三步操作:
(a)使用 native 关键字声明了一个本地方法 stringFromJNI()。
(b)使用 loadLibrary() 方法载入我们编译生成的动态链接库,这里要注意,虽然我们生成的动态链接库名称为 libnative-lib.so,但是此处我们只需要写 native-lib,即就是我们在 CMakeLists.txt 文件中指定的名称,其中的lib前缀和 .so 后缀是系统为我们添加的。
(c)我们在布局文件中放了一个TextView,然后将函数返回的字符串放到了TextView中。
我们对比一下我们声明的native方法和最终我们的ndk帮我们生成的c++代码的函数名:
// 我们声明的 native 方法名
public native String stringFromJNI();
// NDK自动生成的方法名
Java_qu_androidndk_MainActivity_stringFromJNI
可以看出 NDK 生成的方法名是以 Java_包名_类名_方法名的形式,最后可以把已经生成的动态链接库,即 .so 文件拿出来共其他项目调用就可以了,生成目录在 <项目目录>\app\build\intermediates\cmake\debug\obj\...
参考NDK开发初探